 Reactions with water
Reactions with water Reactions with air
Reactions with air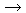 2B2O3(s)
2B2O3(s) Reactions with halogens
Reactions with halogens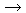 2BF3(g)
2BF3(g)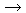 2BCl3(g)
2BCl3(g)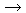 2BBr3(g)
2BBr3(g) Reactions with acids
Reactions with acids|
Compounds | Reactions | Production
|
| Reactions of Boron |
 Reactions with water Reactions with water |
| Boron will not react with water under normal conditions. |
 Reactions with air Reactions with air |
| At higher temperatures, boron does burn in air to form boron(III) oxide, B2O3. |
4B + 3O2(g)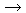 2B2O3(s) 2B2O3(s) |
 Reactions with halogens Reactions with halogens |
| Boron reacts vigorously with fluorine, chlorine, and bromine to form boron(III) trihalides. |
2B(s) + 3F2(g)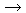 2BF3(g) 2BF3(g) |
2B(s) + 3Cl2(g)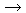 2BCl3(g) 2BCl3(g) |
2B(s) + 3Br2(g)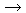 2BBr3(g) 2BBr3(g) |
 Reactions with acids Reactions with acids |
| Crystalline boron does not react with boiling hydrochloric acid (HCl) or boiling hydrofluoric acid (HF). Powdered boron oxidizes slowly when treated with concentrated nitric acid, HNO3. |
| Reduction Potentials | |
| Balanced half-reaction | E0 / V |
H3BO3 + 3H+ + 3e- B(s) + 3H2O B(s) + 3H2O
|
-0.869 |
H2BO3- + 4H+ + 3e- B(s) + 3H2O B(s) + 3H2O
|
-0.687 |
HBO32- + 5H+ + 3e- B(s) + 3H2O B(s) + 3H2O
|
-0.437 |
BO33- + 6H+ + 3e- B(s) + 3H2O B(s) + 3H2O
|
-0.165 |
B(OH)3 + 3H+ + 3e- B(s) + 3H2O B(s) + 3H2O
|
0.87 |
BF4- + 3e- B(s) + 4F- B(s) + 4F- |
-1.04 |
H2B4O7 + 12H+ + 12e- 4B(s) + 7H2O 4B(s) + 7H2O
|
-0.836 |
B4O72- + 14H+ + 12e- 4B(s) + 7H2O 4B(s) + 7H2O
|
-0.792 |